Design Thinking
Design Thinking
In Design Thinking, students learn to be human-centred problem solvers. They identify complex challenges, understand the needs of those around them, and then work in teams to prototype and test innovative solutions that meet those needs.
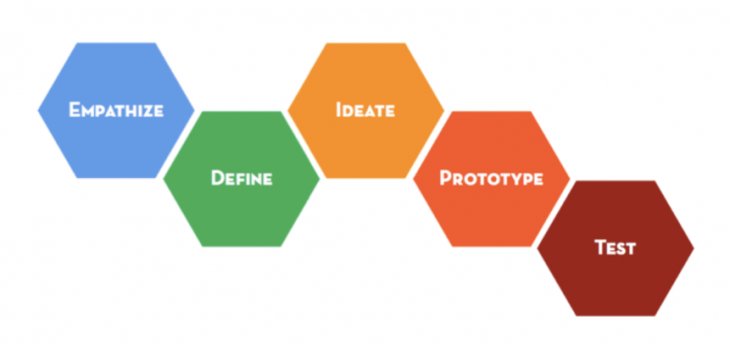
Design Thinking Process
Empathise_
As human-centered designers, students need to understand the people for
whom they are designing. Students learn to build empathy for who they are
and what is important to them.
Define_
Based on a deep understanding of the people they are designing for, students
learn to generate a meaningful challenge – a problem statement from the
designer’s point of view.
Ideate_
At this stage of the process, students focus on idea generation, coming
up with a large number of varied ideas, including wild and unusual ideas.
Prototype and Test_
Students learn to create prototypes, a physical object that people can
interact with and experience for testing and feedback-gathering. These
interactions drive deeper empathy and the iterations help shape successful
solutions.
In the process of solving these problems, students learn empathy, collaborative skills and the value of radical ideas. The following Design Thinking Mindsets are developed:
Human-Centred_
Students exercise empathy for the users they are designing for, and gather
feedback from these users. This is fundamental for good design.
Radical Collaboration_
Students work in mixed groups and leverage on different viewpoints to
generate creative ideas and realise their design.
Mindful of Process_
Students know where they are in the design process at any time, what methods
to use in that stage, and what their goals are.
Embrace experimentation_
Students build as a way to think and learn.
Bias Toward Action_
Students learn to do and make, rather than just think and meet.
Design Thinking Curriculum
The CWSS Design Thinking Curriculum is taught as a spiral progression from Secondary One to Three.
Secondary One: Students experience mindset-building sessions and short design sprints to introduce them to design thinking.
Secondary Two: Students take on a more rigorous design challenge which will deepen their learning and through their application of the design thinking mindsets and skills. The challenge requires students to address a need in the school or community.
Secondary Three: Students initiate their own design challenges with their CCAs as they work together to plan for their Values-In-Action (VIA) Projects using the Design Thinking approach.
Design Thinking for School Improvement
In addition to being a key programme for students, staff the school also employs the design thinking approach to drive innovation and continuous improvement.
The school has applied design thinking in the following areas:
• Developing innovative spaces including the Imaginarium (school library), the D.space (school makerspace), the Asgard (school canteen)
• Transforming school programmes and events, including the lower secondary science Farm-to-Table programme, the TrailBlazer Festivals and the annual Open House
• Streamlining school work processes, including data management, administrative workflows
MOE Innergy Award 2024
· Silver: Farm-to-Table (FTT) Programme for Lower Secondary Science
· Bronze: Champions in Action (CIA)

